Gen AI Trends in Supply Chain Digital Transformation
With Generative AI guiding the path, AI is set to infuse a whopping $15.7 trillion into the worldwide economy. Analysts anticipate that by 2024, half …
READ MORETypically, when creating software applications we need to deal with multiple resources, having to deal with sensitive information like database connection strings and storage connection strings are obvious in these situations. Maintaining these sensitive information in a secure manner is always a primary concern of any engineering team.
With Microsoft Azure, we can use Managed Identities to secure these types of sensitive information.
What is a Managed identity?
Managed identities provides Azure services with an automatically managed identity in Azure Active Directory.
You can use this identity to authenticate to any service that supports Azure AD (Active Directory) authentication, without having to store the credentials in your code.
Azure Managed Identities comes in two flavours.
To get a better understanding of these two flavours of managed identities. Let's take a look at a typical example of a web application which consumes a database.
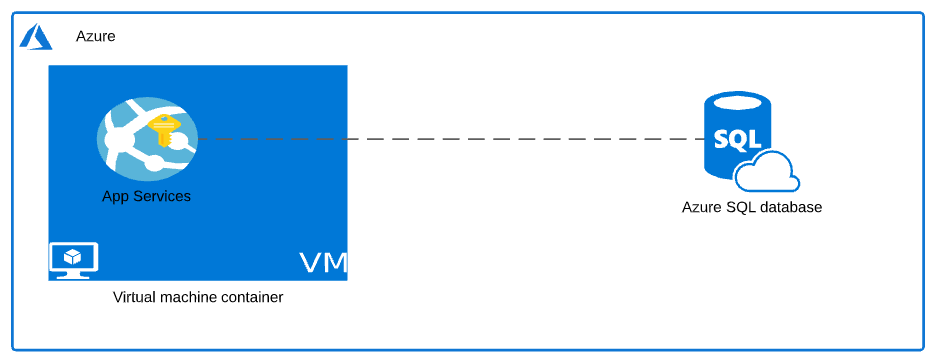
The above diagram shows a very basic way as to how an Azure App Service can consume a database, simply by managing the connection string in the application settings file.
Of course we can use Azure KeyVault service to manage the application secrets and consume the database service from your Azure AppService as a more elegant approach.
As we are in the look out for an even better way to make the application more secure and to seamlessly manage service principal key rotation and lifecycle management. Let's take a look at System-Assigned Azure Managed Identity Service.
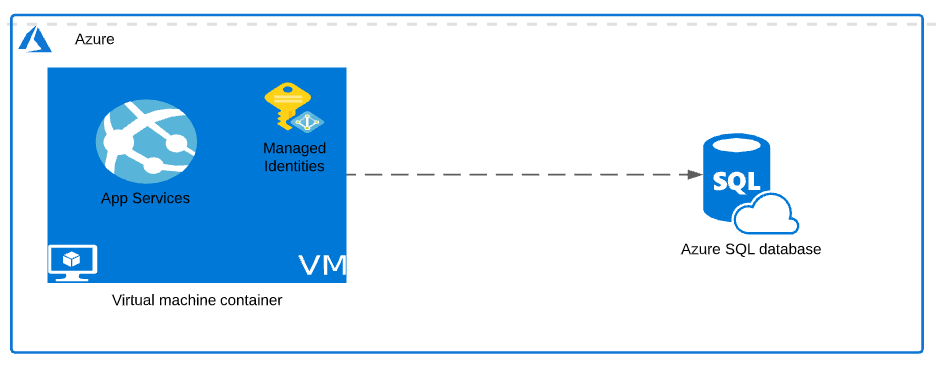
Once the identity is created in Azure Active Directory, you can use this identity to grant access to the target resources (In this case the Azure SQL Database) which support Azure AD authentication.
As you can see in the above diagram, the managed identity is tightly attached to the VM. With that now the authentication to the sql server instance is handled automatically via the virtual machine itself. As there are no application secrets managed outside of the Azure environment this approach is much more secure.
You can think of Azure Managed Identity as a special type of service principals which provides the below advantages.
1. Automatic service principal credential rotation.
2. Better identity lifecycle management.
System-assigned azure managed Identities are tightly coupled to the resource which it is attached to and gets destroyed when the primary resource to which it is attached gets destroyed. also, you no longer have to worry about the service principal expiration or credential rotation. All those are handled automatically by Azure for you.
Now since we know what the System-assigned Azure Managed Identities are, Let's move onto the other type of Managed Identity service which is the User-Assigned Azure Managed Identities.
Let's use the below mentioned scenario to grasp what a System-assigned Azure Managed Identities is.
Now, assume that the company started growing in business, which means now we have a few extra VM’s to manage the user load, and we still need to consume the same target SQL server instance from all these VM’s. In this situation, we can use a User-Assigned Azure Managed Identity feature provided in Microsoft Azure as it is loosely coupled and supports attaching to multiple sources and targets.
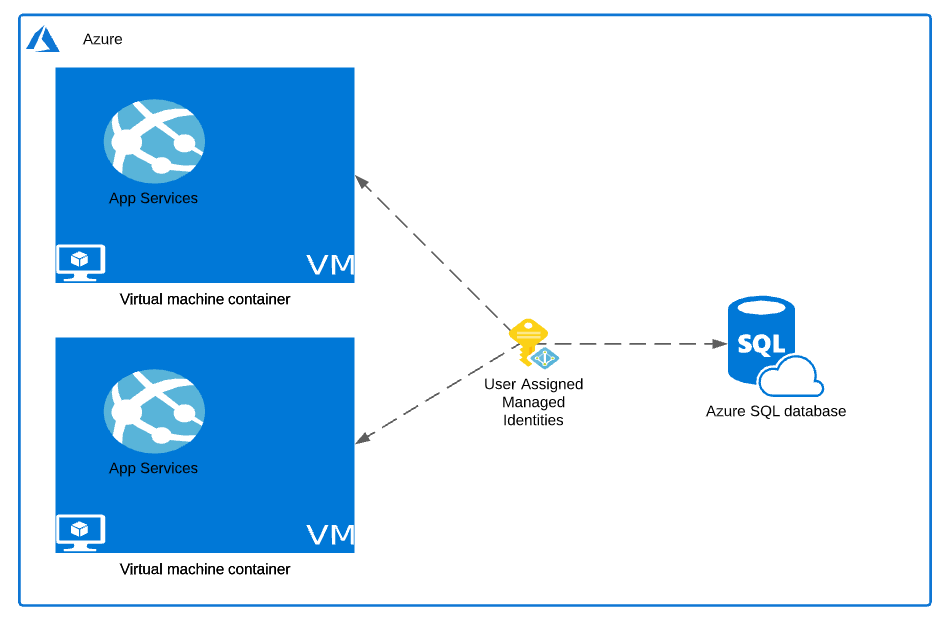
With User-Assigned Azure Managed Identities, it creates an identity independent of the lifecycle of the Azure resource. As and when the new resources get spun up, we just need to assign the identity to the new resources that got created. Once the identity is assigned and granted the required permissions, your application will continue to authenticate and work as before.
As the user-assigned managed identities are created independent of the resource and do not get deleted when the attached resources get deleted, therefore, it is your responsibility to manage the life cycle of the generic identities.
Adding the identity to a new resource can be done in just a few minutes and it's more secure as the credentials are managed within the Azure infrastructure itself and it is more flexible due to its loosely coupled, independent nature.
Here is a comparison between System-Assigned Managed Identity and User-Assigned Managed Identity.
| System-Assigned Managed Identity | User-Assigned Managed Identity |
|---|---|
| Created With Azure Resource | Created Independently |
| Automatic Identity Lifecycle Management | Manual Identity Life Cycle Management |
| Can not be shared with Multiple Sources | Can be shared with Multiple Sources |
To conclude:
Azure Managed Identities provides endless possibilities and ways for you to securely manage your application credentials inside your organization.
Hope this article gives you an idea of Azure Managed Identity, the different flavours of Managed Identity, comparison of its features and in what sort of situations we can use each of these flavours.
Thank you for your time...
With Generative AI guiding the path, AI is set to infuse a whopping $15.7 trillion into the worldwide economy. Analysts anticipate that by 2024, half …
READ MOREIntoday’s digital landscape, where data is more valuable than ever, understanding the tools and technologies that enable efficient data management and …
READ MORE