Better Defect Reduction: AI Applications in Your Quality Engineering Maturity Journey
The next time you sit down with your Chief Innovation Officer, bring up quality maturity as an agenda item. Artificial intelligence (AI) exists with …
READ MOREThe pandemic has accelerated digital health entrepreneurs, leading to increased adoption of cloud computing to facilitate a patient-centric healthcare. Cloud-based solutions aim to reduce costs, streamline operations, and improve patient care. However, concerns about security, legal compliance, and potential downtime must be addressed. As we progress in 2024, we now need secure and dependable virtual access to healthtech consultants to navigate and address the 21st-century’s challenges and objectives.
Cloud computing has significantly impacted the healthcare sector by lowering expenses, and simplifying operations to create a patient-centric healthcare sector. It allows easy access to data and apps, enabling better decision-making and enhancing care quality. Cloud-based technologies automate administrative tasks, saving on hardware, software, and maintenance costs. Health Information Exchange (HIE) platforms, used by insurance companies, hospitals, and clinics, offer cost savings, accessibility, and flexibility. These cloud-based solutions also eliminate the need for on-site data centers, reducing energy expenses.

When referring to IT systems and resources, the terms “Distribution” and “Deployment” are frequently used in the healthcare sector. Both discuss how healthcare institutions provide technological solutions:
Distribution Model: The delivery of healthcare applications and data to end consumers is the main emphasis of distribution. This may entail techniques such as software installation on personal devices or granting access via an online portal.
Deployment Model: The location and administration of the underlying infrastructure that supports healthcare applications are referred to as deployment. These could be cloud-based resources, on-site servers, public servers, or a hybrid setup.
The top 5 trends that support healthcare sector to expand the breadth of cloud offerings and capabilities, accelerating growth across all segments in the public cloud services are listed below:
Healthcare organizations use data analytics tools to enhance patient experience, with Truven Health Analytics revealing that mistakes and delays lead to decreased satisfaction, postponed follow-ups, and reluctance to continue treatments.
Healthcare organizations are shifting from general data analytics to specialized analytics in 2024 to improve patient experience and operational effectiveness. Cloud computing can provide dependable access to devices, apps, and data, enhancing patient satisfaction. However, data privacy, system interoperability, and strong security measures are crucial for maximizing the use of healthcare data.
According to KPMG, a 15% to 25% rise in customer ratings has been observed by firms that have used cloud technology. That means that the higher patient retention rates will result in savings of millions of dollars.
Legacy systems hinder healthcare’s digital revolution, forcing 70% of businesses to adopt cloud computing. However, improper implementation can cause a huge burden for patients and doctors, highlighting the need for adaptability and scalability of the infrastructure.
Cloud systems facilitate real-time data sharing and collaboration in modern healthcare, offering flexibility in offering services and managing large data volumes. They enable hospitals to handle finances, respond quickly to technological advancements, and prioritize patient care over paperwork. Despite high costs and interoperability issues, cloud computing offers advantages to electronic medical records while eliminating disadvantages.
Healthcare systems are transitioning from compartmentalised to interconnected ecosystems in 2024. This shift ensures seamless information flow across coordinated care, improving patient experience and health outcomes. Dispersed health information on various devices can pose challenges in emergencies.
The strategy involves reducing unique software and combining systems from other hospitals and healthcare providers. Early stakeholder involvement enhances IT compatibility and a technology-focused strategy plan facilitates seamless migration. Cloud storage and interoperability ensure patient data accessibility across platforms, simplifying communication and communication between family members and healthcare providers.
Manual, labor-intensive processes are gradually going away. The use of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) is expanding, transforming everything from patient scheduling to diagnosis and treatment plans. In addition to having rapid access to test findings and photos, doctors can make quick and efficient changes to an electronic medical record without having to send the information over a network or save it for printing. This implies that patients don’t have to wait for updated information to reach their caregivers.
Automation and AI are also transforming patient scheduling, diagnosis, and treatment plans. Automation allows quick access to test findings and photos, reducing waiting times for patients. However, healthcare organizations must use AI cautiously, as it is still in its experimental stages. AI testing and validation are needed to make AI applications more reliable. Thus, cloud technology offers cost reductions and improved performance.
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and safety in healthcare transactions, reducing costs and facilitating efficient sharing of financial information among providers.
Blockchain technology has the potential to improve healthcare by managing transactions and medical records in a transparent and safe manner. Patients may have more control over their data as a result. But overcoming complicated restrictions and establishing clear interoperability guidelines for how various systems communicate still remain challenged. On the other hand, cloud computing offers quicker recovery times and automated backups, which makes it a useful tool for enhancing data security and accessibility in the healthcare sector.

Apart from the above trends, according to Gartner, Inc., four more new trends in cloud computing are boosting growth across all market sectors for public cloud services by broadening the scope of cloud offerings and capabilities. The four trends are as follows:
Cloud ubiquity refers to the widespread availability and accessibility of cloud computing services, which can revolutionize the healthcare sector. Cloud technology improves accessibility, scalability, and flexibility in medical research, personalized medicine, and real-time patient monitoring, fostering growth in telehealth and remote care services.
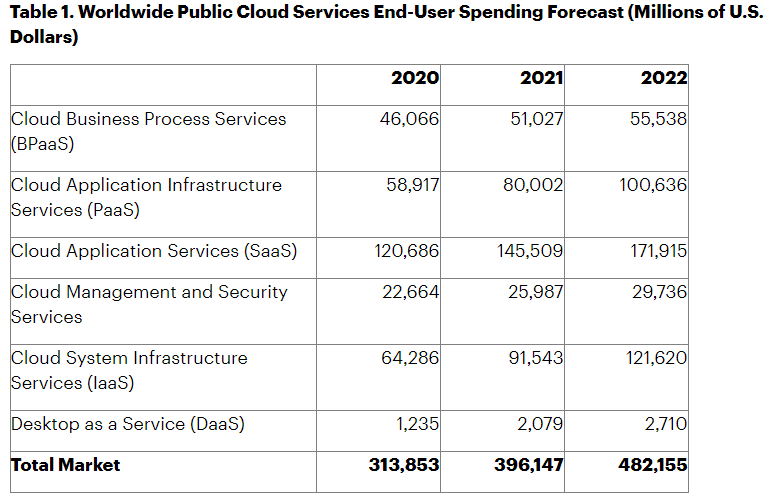
Worldwide Public Cloud Services End-User Spending Forecast (Millions of U.S. Dollars). Source: Gartner, Inc.
Regional cloud ecosystems are cloud computing environments specific to a geographical area, driven by factors like geopolitical concerns, regulatory fragmentation, and industry needs. Regional cloud ecosystems in a patient-centric healthcare ensure local regulations, data privacy, and security by reducing vendor lock-in, improving data sovereignty, and enhancing patient information security.
The adoption of a carbon-intelligent cloud in a patient-centric healthcare in sector is a growing focus on sustainability. Healthcare organizations can reduce their carbon footprint, optimize costs, and attract patients and staff by choosing providers with strong sustainability practices for cloud services.
Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services (CIPS) providers offer cloud computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and networking as a service. Gartner anticipates healthcare organizations adopting Automated Programmable Infrastructure (API) solutions, resulting in reduced IT costs, improved agility, scalability, simplified management, and enhanced security for patient data protection.
Although there are clear benefits to having information available at all times and places, there are challenges to be addressed. Public cloud adoption in healthcare has long been hampered by possible security threats and worries about compliance. IT personnel are responsible for maintaining network uptime, scheduling software updates on time, and implementing a reliable backup schedule.
Healthcare companies must also think about how a third party will handle their data, look into the companies that their cloud partners interact with, and make sure that any cloud networks they utilize adhere to security standards. As the sector rises to face these difficulties, cloud providers having a background in healthcare and an awareness of the particular regulatory landscape will be given preference. The world’s most cutting-edge healthcare firms have announced significant cloud efforts after careful consideration and research, which should provide everyone with a sense of comfort. One such instance is the Mayo Clinic’s announcement of its collaboration with Google.

Looking for features is one of the most crucial things to keep in mind when selecting a cloud-based system. Encryption is one of these characteristics, as is seeing if your service protects from both external and internal threats. With encryption of data, it is possible to receive absolute guarantee, which means that no information on the account may be seen by such person who got access to your account. Encryption can be done using one of the two protocols that is Transport layer security (TLS) and secure sockets layer (SSL).
Although the SSL enables the enhancement of security since it is used to encode information, while it travels between servers and computer networks, TLS is designed to protect data exchange between two endpoints. It is also important to note that in case one fails, you should have also have technological as well as physical contingency strategies.
Although the rise in digital healthtech platforms has been seen as a positive development, there are two sides to the growing popularity of digital health platforms. They provide great solutions for storing, classifying, and even sharing your records, on one hand. However, such platforms also create several concerns and questions related to safety and privacy of data which will have to be addressed.
To avoid compromising the data integrity regarding the privacy and security standards, be cautious of HIPAA compliance by investigating the platforms for information safety and checked compliance status. It is possible to manage the settings regarding information sharing to ensure proper security and only allow people with the right permissions to have permissions to access the information. Find other health data management platforms with enhanced levels of encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure logging in measures. It is also a good practice to regularly backup health data on a separate, secure device ensures control over information even if the primary platform fails.
It is anticipated that by the end of 2024, healthcare technology will undergo a dramatic change as we embrace AI and Blockchain to increase efficiency and sustainability.
Healthcare has entered an era where it is more intelligent, patient-centric, and interconnected than ever before. Therefore, companies in the healthcare sector will be better equipped to survive and grow in this rapidly changing environment if they accept these changes and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The next time you sit down with your Chief Innovation Officer, bring up quality maturity as an agenda item. Artificial intelligence (AI) exists with …
READ MOREAI has been an anticipated technological breakthrough, taking over most manual white-collar jobs today. PwC’s Global AI Study reveals that AI will …
READ MORE